During the Physical Examination, we use the information we gather from your Interview to estimate the cause of your complaint and to determine what is the best treatment we can provide.
**Physical examinations are also performed on those who have no particular pain and wish to relax. The purpose of this examination is to provide a comprehensive check of the whole body in order to propose an effective method of treatment for relaxation.
Range of Motion Test
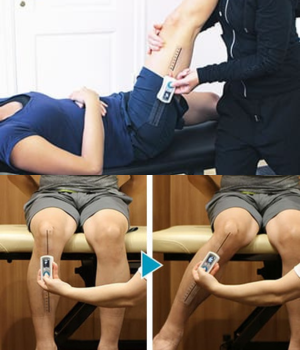
Range of motion (ROM) means the extent or limit to which a part of the body can be moved around a joint or a fixed point; the totality of movement a joint is capable of doing.
The purpose of ROM exercises are prevention the development of adaptive muscle shortening, contractures, and shortening of the capsule, ligaments, and tendons. ROM exercises also provide sensory stimulation.
Limited ROM refers to a joint that has a reduction in its ability to move. Motion may be limited because of a problem within the joint, swelling of tissue around the joint, stiffness of the muscles, or pain.
Range of motion can be maintained and gradually increased through range of motion & stretching exercises.
Manual Muscle testing
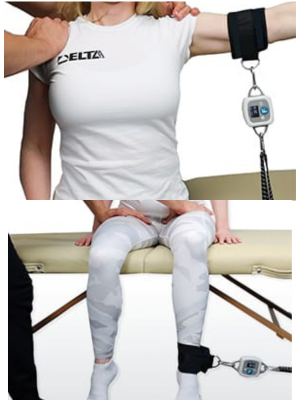
Manual muscle testing is used in rehabilitation and recovery to evaluate contractile units, including muscles and tendons, and their ability to generate forces. This is an important evaluative tool to assess impairments and deficits in muscle performance, including strength, power, or endurance.
Impairments in muscle function may result from a number of issues, including:
- Musculoskeletal injuries
- Joint mobilization for extended period of time
- Inactivity
- Neuromuscular disease or disorders
Identifying impairment in specific muscles or muscle groups is an important part in determining the course of rehabilitation which may include therapeutic exercise, manual therapy, bracing, or functional movement training.
Special tests

There are many ‘special tests’, that are used by clinicians in orthopedics / orthopedics in general, during a physical examination. These tests are used to rule in or out specific musculoskeletal problems. They help in the differential diagnosis of orthopedic conditions and injuries.
There are many such clinical orthopedic tests that target the various regions of the body and many tissue types including connective tissue, muscles, nerves, bones (actually a specialized connective tissue), vascular structures, etc.
Neurological Exam

A neurological exam, also called a neuro exam, is an evaluation of a person's nervous system that can be done in the healthcare provider's office. It may be done with instruments, such as lights and reflex hammers. It usually does not cause any pain to the patient. The nervous system consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and the nerves from these areas. There are many aspects of this exam, including an assessment of motor and sensory skills, balance and coordination, mental status (the patient's level of awareness and interaction with the environment), reflexes, and functioning of the nerves. The extent of the exam depends on many factors, including the initial problem that the patient is experiencing, the age of the patient, and the condition of the patient.
Functional Movement Screen

The Functional Movement Screen (FMS) is a tool used to identify asymmetries which result in functional movement deficiencies. The FMS aims to identify imbalances in mobility and stability during seven fundamental movement patterns. These movement patterns are designed to provide observable performance of basic locomotor, manipulative and stabilising movements by placing an individual in extreme positions where weaknesses and imbalances become noticeable if appropriate mobility and motor control is not utilised.
1. Deep Squat
2. Hurdle Step
3. In-line Lunge
4. Active Straight-leg Raise
5. Trunk Stability Push-up
6. Rotary Stability
7. Shoulder Mobility
